## 介绍
图是最有用的数据结构之一。它们可用于对几乎所有事物进行建模——对象关系和网络是最常见的。图像可以表示为网格状的像素图,句子可以表示为单词的图。图表被用于各个领域,从制图到社会心理学,当然它们在计算机科学中也被广泛使用。因此图搜索和遍历起着重要的计算作用。Dijkstra 算法 旨在找到 图中节点 之间的最短路径。它是由荷兰计算机科学家 Edsger Wybe Dijkstra 于 1956 年在思考从鹿特丹到格罗宁根的最短路线时设计的。Dijkstra 算法 多年来一直在发生变化,并且存在各种版本和变体。最初用于计算两个节点之间的最短路径。由于它的工作方式 ,适用于计算起始节点和图中每个其他节点之间的最短路径。这种方式可用于生成 最短路径树 ,该树由两个节点以及所有其他节点之间的最短路径组成。然后你可以修剪掉你不感兴趣的树,得到两个节点之间的最短路径,但你不可避免地必须计算整个树,这是 Dijkstra 算法 的一个缺点,它不适合大型图。
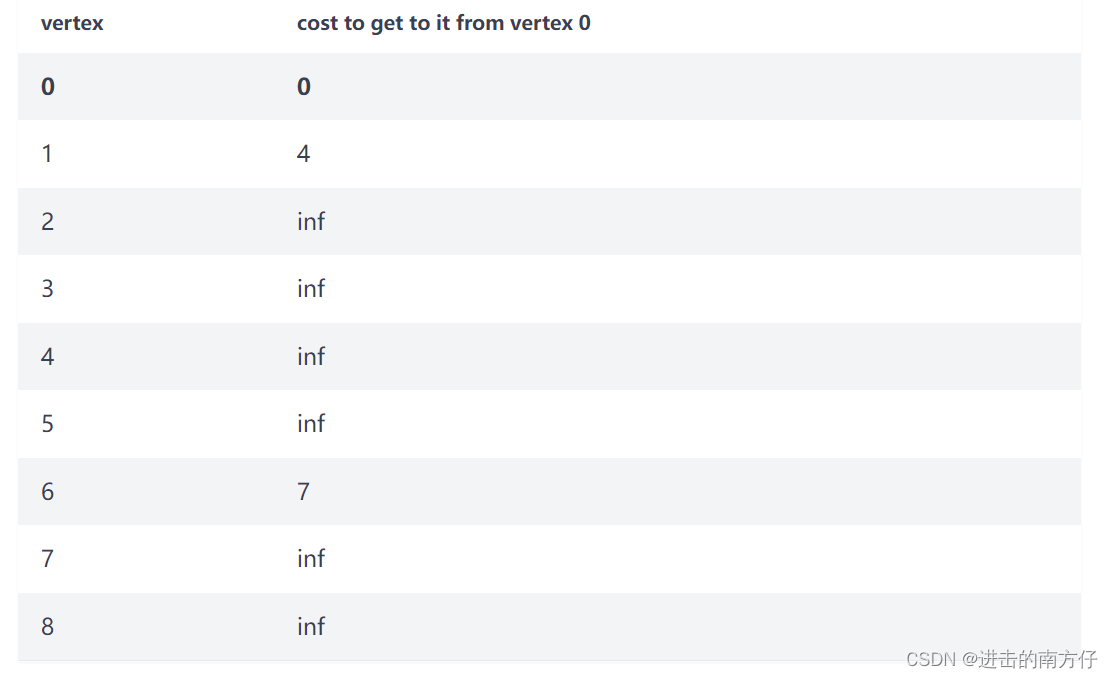
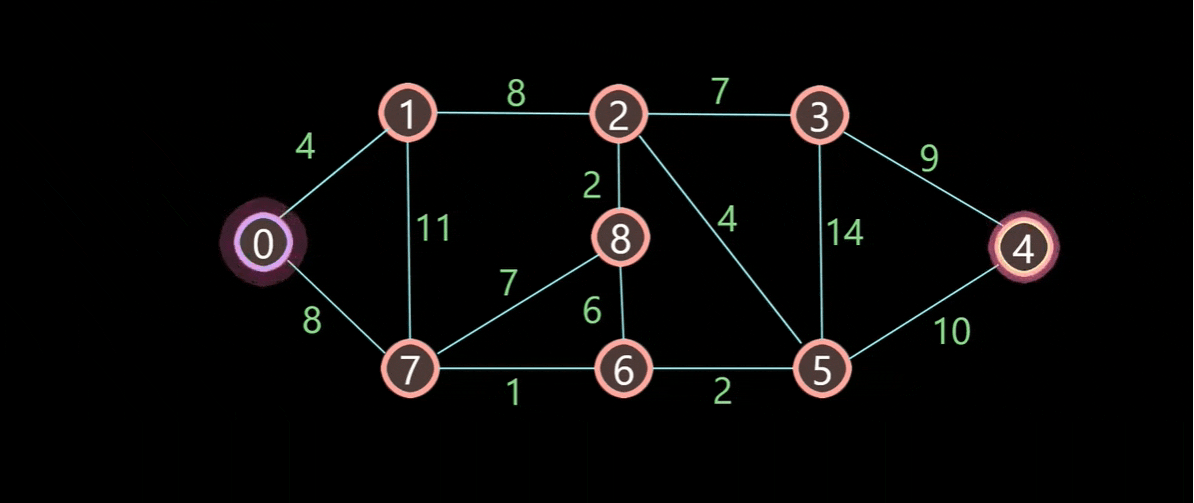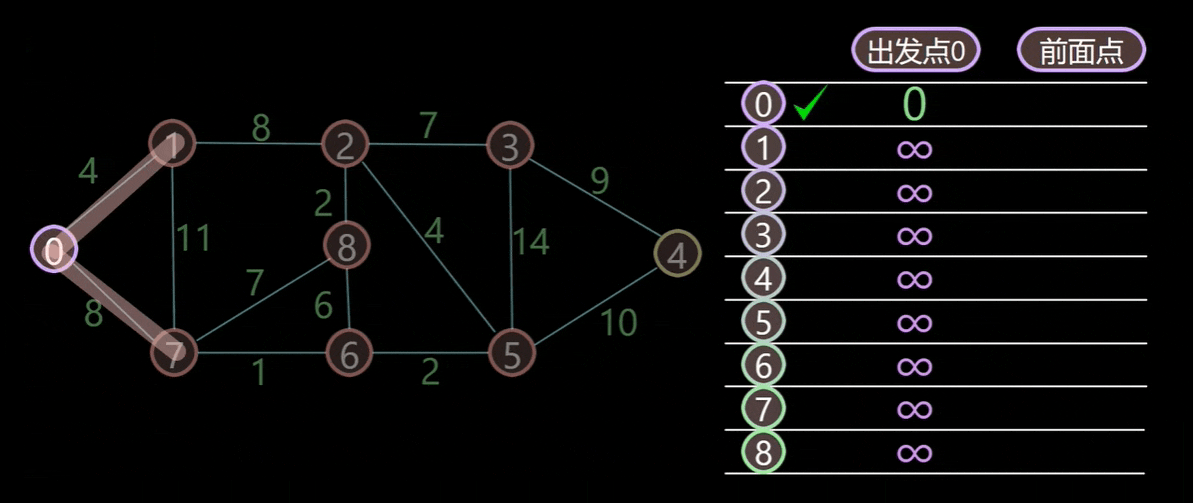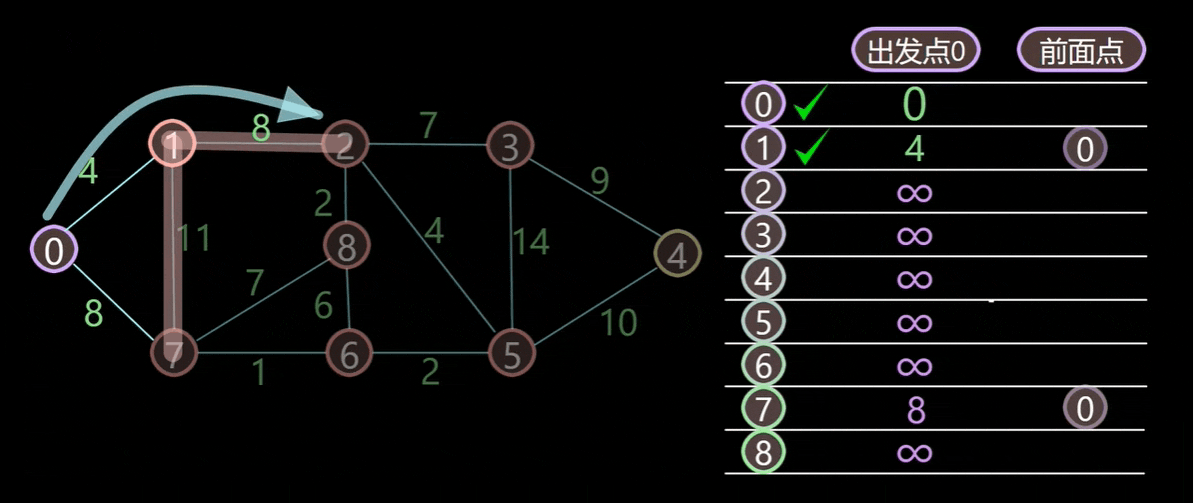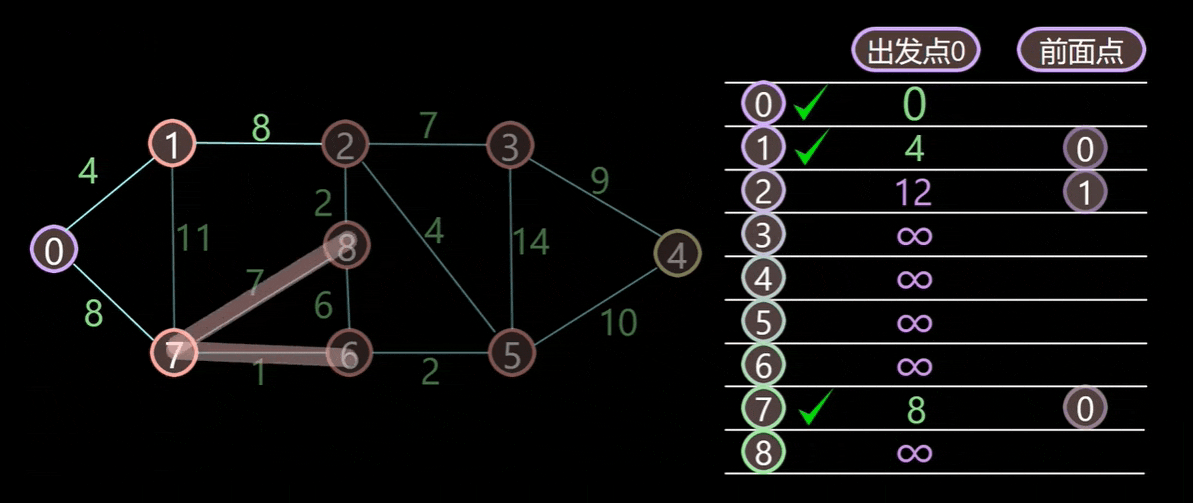
Dijkstra 算法 Dijkstra 算法 适用于无向、连接、加权图,Dijkstra 算法 可以求出源节点到其他所有节点的最短路径。“无穷大(inf)” ,以确保我们可以与之比较的所有其他成本都小于起始成本。唯一的例外是第一个起始顶点的成本——这个顶点的成本为 0,因为它没有通往自身的路径——标记为 源节点 s。然后依据以下三个规则,直到遍历整个图:
每次从未标记的节点中选择距离出发点最近的节点,标记,收录到最优路径集合中。
对于当前节点 n 和其的邻居节点 m 如果 cheapestPath(s, n) + cheapestPath(n, m) < cheapestPath(s, m),则更新 s 到 m 的最短路径为 cheapestPath(s, n) + cheapestPath(n, m)。
且每次更新最短路径时会保存该节点的前节点。
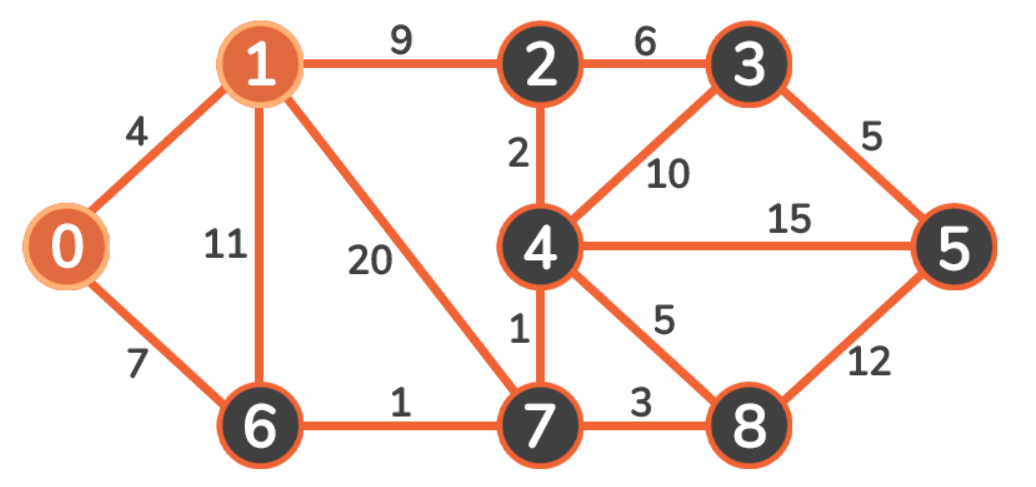
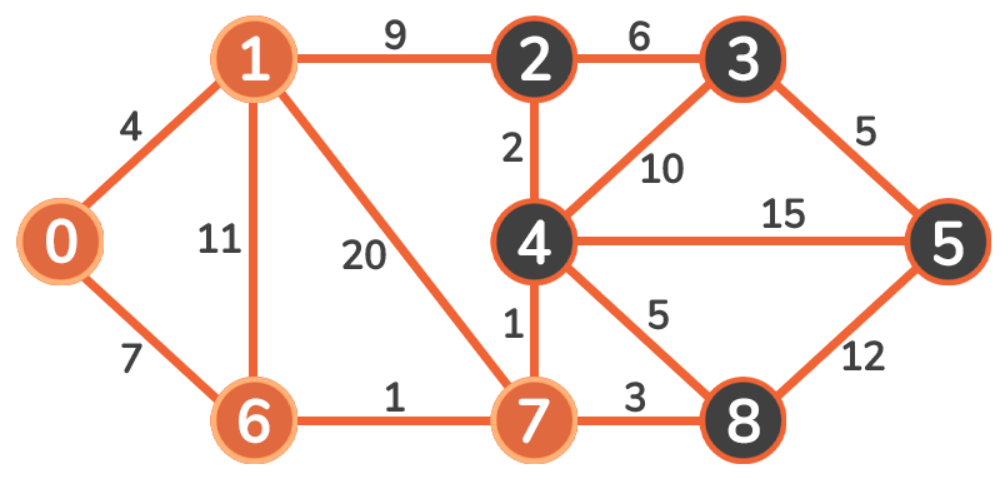
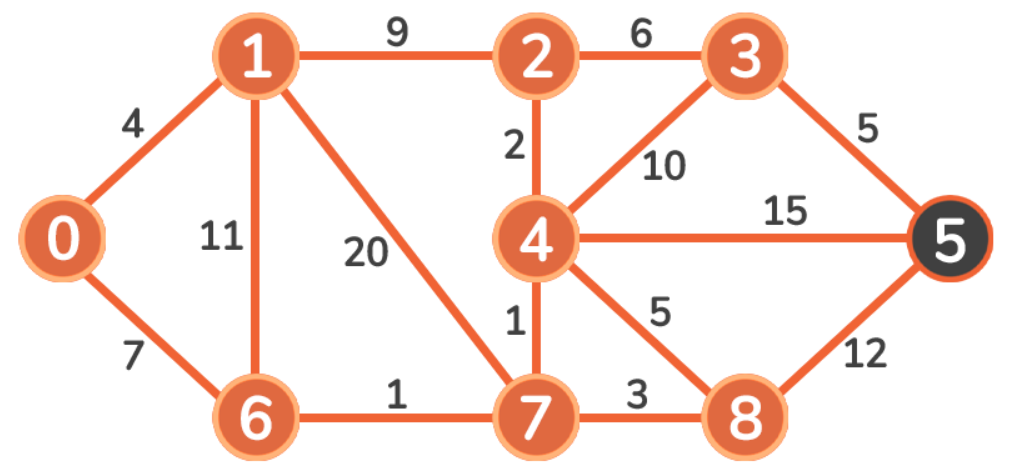
下面用一个无向、加权、连通图来解释上述规则原理:
0 + 4 < infinity 和 0 + 7 < infinity,我们更新这些顶点的成本:4 < 7,所以我们遍历到 Vertex 1:
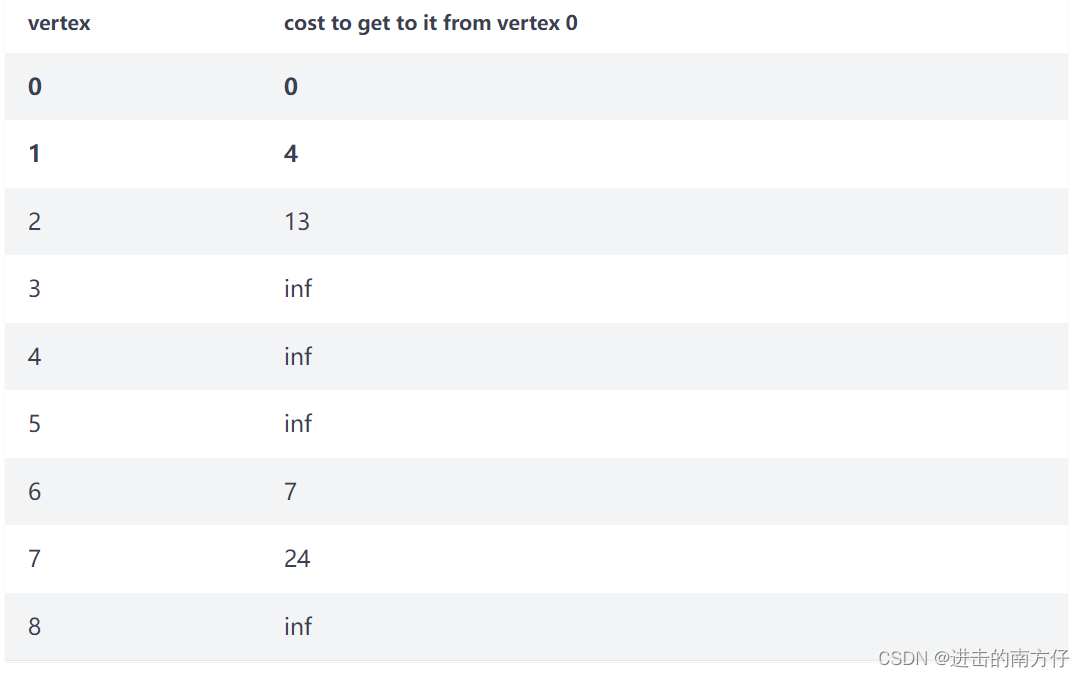
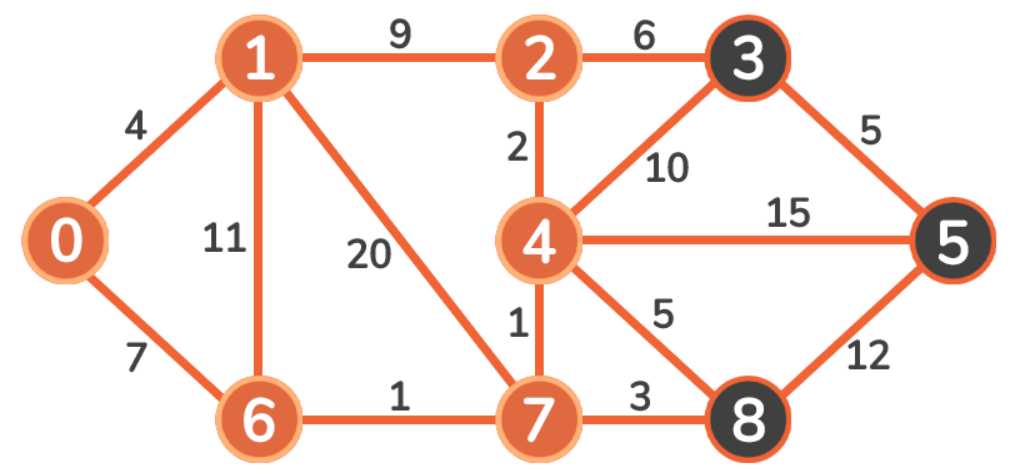
因为 4 + 9 < infinity,Vertex 2 的新成本将是 13。
因为 4 + 11 > 7,Vertex 6 的成本将保持为 7。
因为 4 + 20 < infinity,Vertex 7 的新成本将是 24。
则新成本如下:
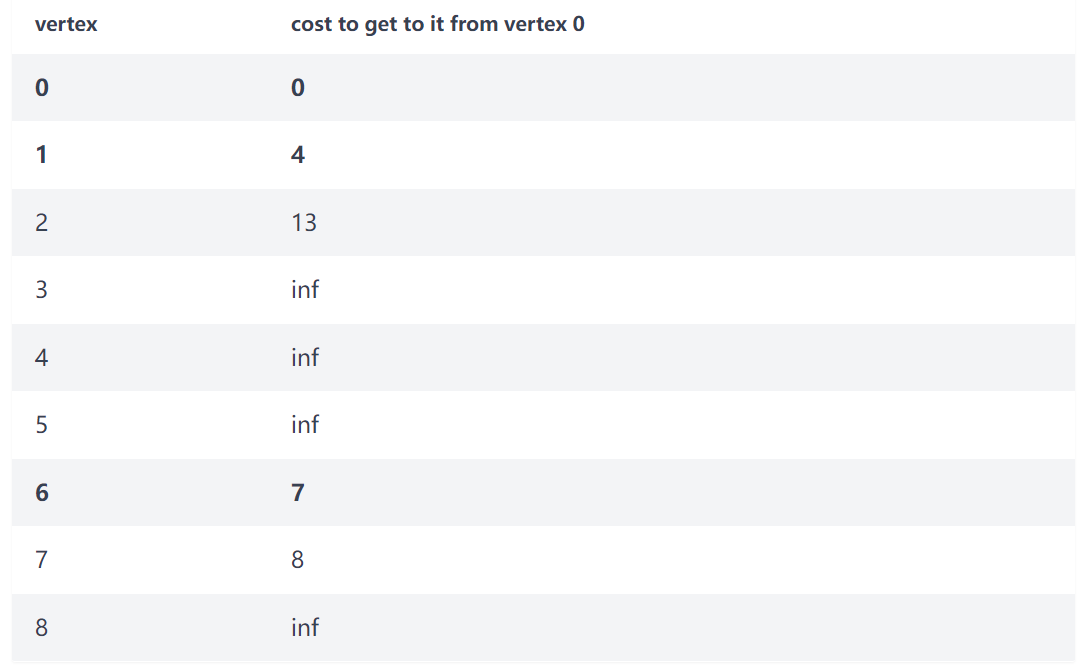
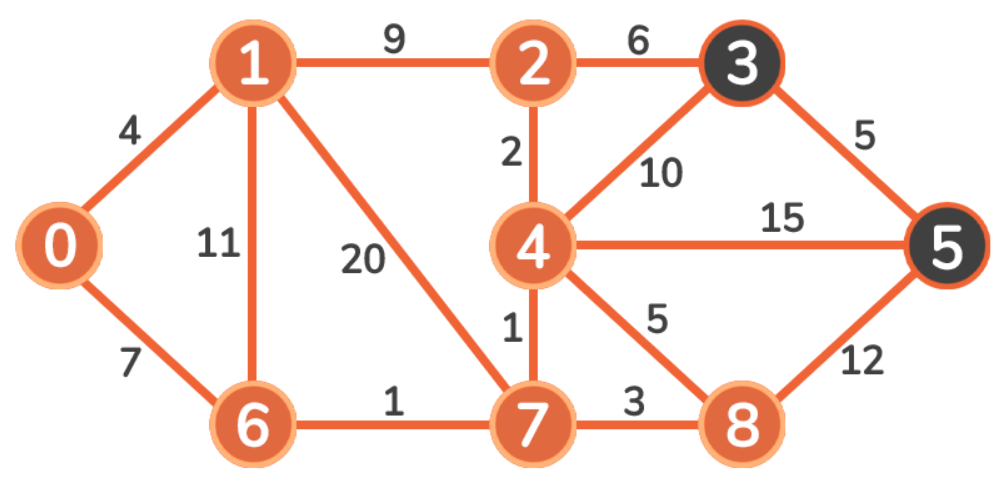
该过程继续到 Vertex 7:11 + 6 < 19,Vertex 3 的成本被更新。然后继续到 Vertex 8。
然后更新 Vertex 3:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JLARzu7coEs
Python 实现 Dijkstra 算法 为了对我们还没有访问过的顶点进行排序和跟踪——我们将使用 PriorityQueue(优先队列) :
1 from queue import PriorityQueue
实现一个名为 Graph 的类的构造函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 class Graph : def __init__ (self, num_of_vertices ): self.vertices = num_of_vertices self.edges = [[-1 for i in range (num_of_vertices)] for j in range (num_of_vertices)] self.visited = []
在这个简单的参数化构造函数中,将图中顶点的数量作为参数,并初始化了三个字段:
vertices:表示图中的顶点数。edges:以矩阵的形式表示边的列表。对于节点 u 和 v,self.edges[u][v] = weight。visited:将包含访问的顶点的集合。
定义一个将向图形添加边的方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 def add_edge (self, u, v, weight ): self.edges[u][v] = weight self.edges[v][u] = weight
定义 Dijkstra 算法 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 def dijkstra (self, start_vertex ): D = {v: float ('inf' ) for v in range (self.vertices)} D[start_vertex] = 0 pq = PriorityQueue() pq.put((0 , start_vertex)) previousVertex = {} while not pq.empty(): (dist, current_vertex) = pq.get() self.visited.append(current_vertex) for neighbor in range (self.vertices): if self.edges[current_vertex][neighbor] != -1 : distance = self.edges[current_vertex][neighbor] if neighbor not in self.visited: old_cost = D[neighbor] new_cost = D[current_vertex] + distance if new_cost < old_cost: pq.put((new_cost, neighbor)) D[neighbor] = new_cost previousVertex[neighbor] = current_vertex return D, previousVertex
在这段代码中,首先创建了一个大小为 num_of_vertices 的字典 D,用于统计最短路径的成本。整个列表初始化为无穷大。这将是一个列表,我们在其中保留从 start_vertex 所有其他节点的最短路径。我们将起始顶点的值设置为 0,因为这是它与自身的距离。然后,我们初始化一个优先级队列,我们将使用它来快速将顶点从最远到最远排序。我们将起始顶点放入优先级队列中。再然后初始化previousVertex ,用于标记每个节点的前节点。现在,对于优先队列中的每个顶点,我们将首先将它们标记为已访问,然后我们将遍历它们的邻居。如果邻居没有被访问,我们将比较它的旧成本和新成本。旧代价是从起始顶点到邻居的最短路径的当前值,而新代价是从起始顶点到当前顶点的最短路径与当前顶点到相邻顶点的距离之和的值邻居。如果新成本低于旧成本,我们将邻居及其成本放入优先级队列,并相应地更新我们保留最短路径的列表,同时更新邻居节点的前节点。最后,在所有顶点都被访问并且优先级队列为空之后,我们返回字典 D 和 previousVertex 。
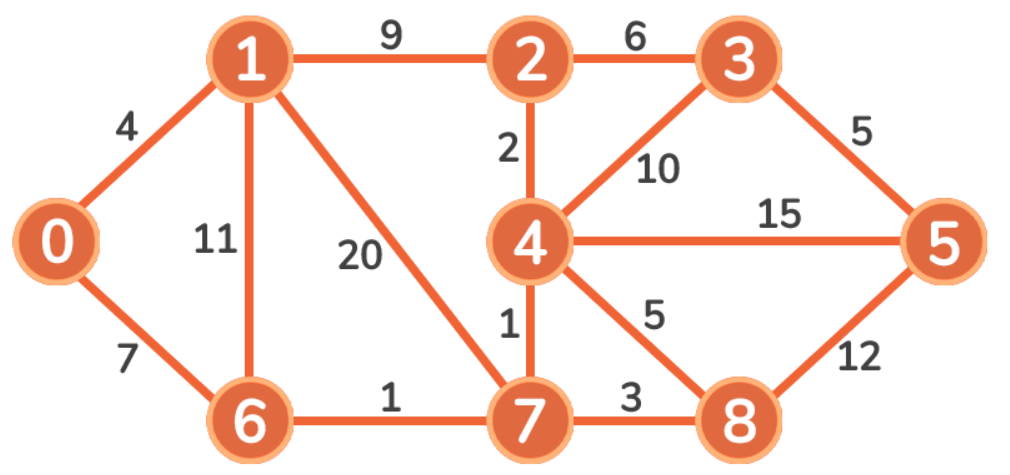
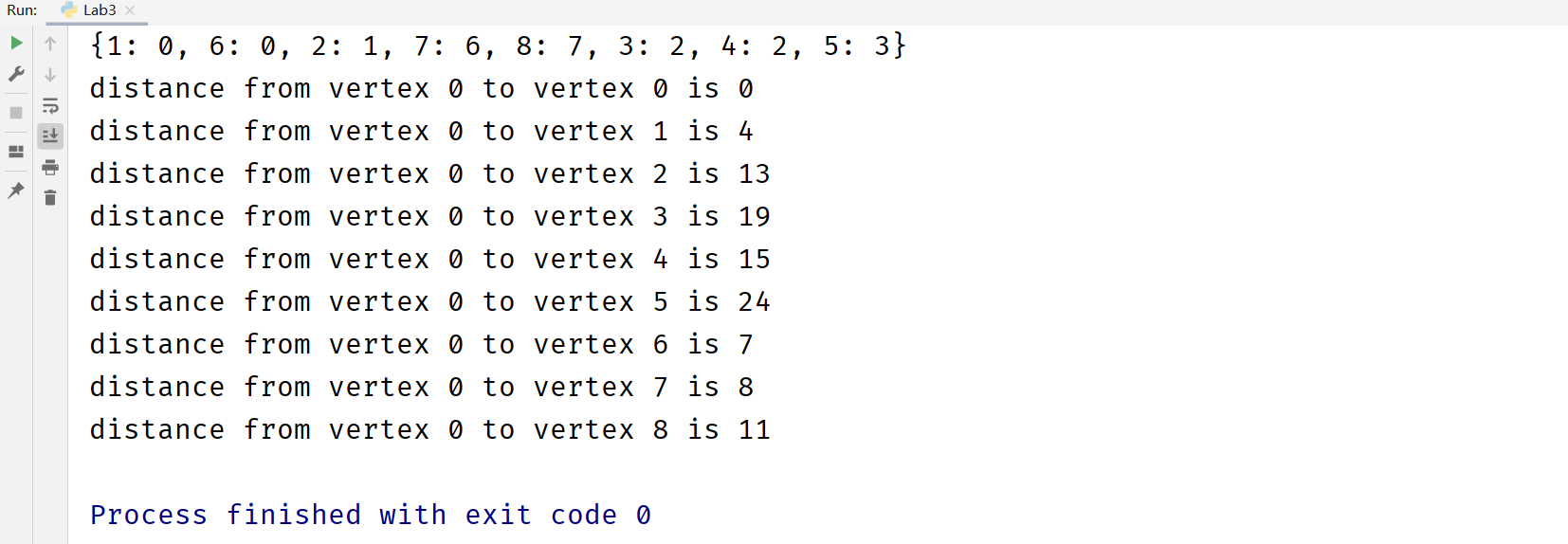
实现之前的例子:
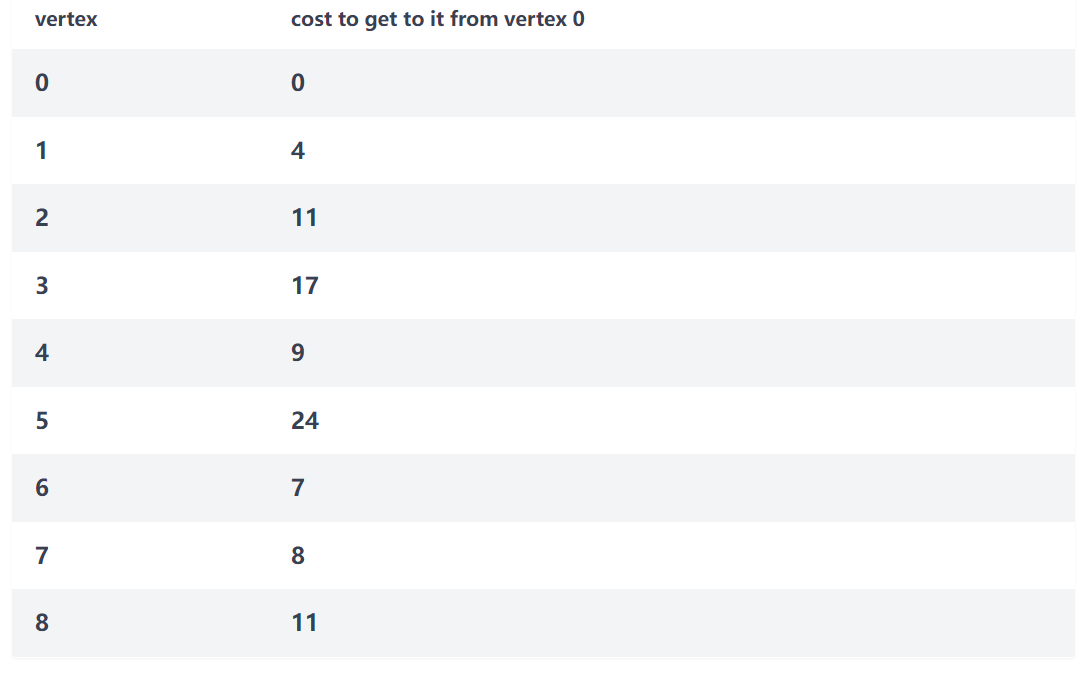
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 def Dijkstra () : g = Graph(9 ) g.add_edge(0 , 1 , 4 ) g.add_edge(0 , 6 , 7 ) g.add_edge(1 , 6 , 11 ) g.add_edge(1 , 7 , 20 ) g.add_edge(1 , 2 , 9 ) g.add_edge(2 , 3 , 6 ) g.add_edge(2 , 4 , 2 ) g.add_edge(3 , 4 , 10 ) g.add_edge(3 , 5 , 5 ) g.add_edge(4 , 5 , 15 ) g.add_edge(4 , 7 , 1 ) g.add_edge(4 , 8 , 5 ) g.add_edge(5 , 8 , 12 ) g.add_edge(6 , 7 , 1 ) g.add_edge(7 , 8 , 3 ) D, previousVertex = g.dijkstra(0 ) print (previousVertex) for vertex in range (len (D)): print (f"distance from vertex {0 } to vertex {vertex} is {D[vertex]} " )
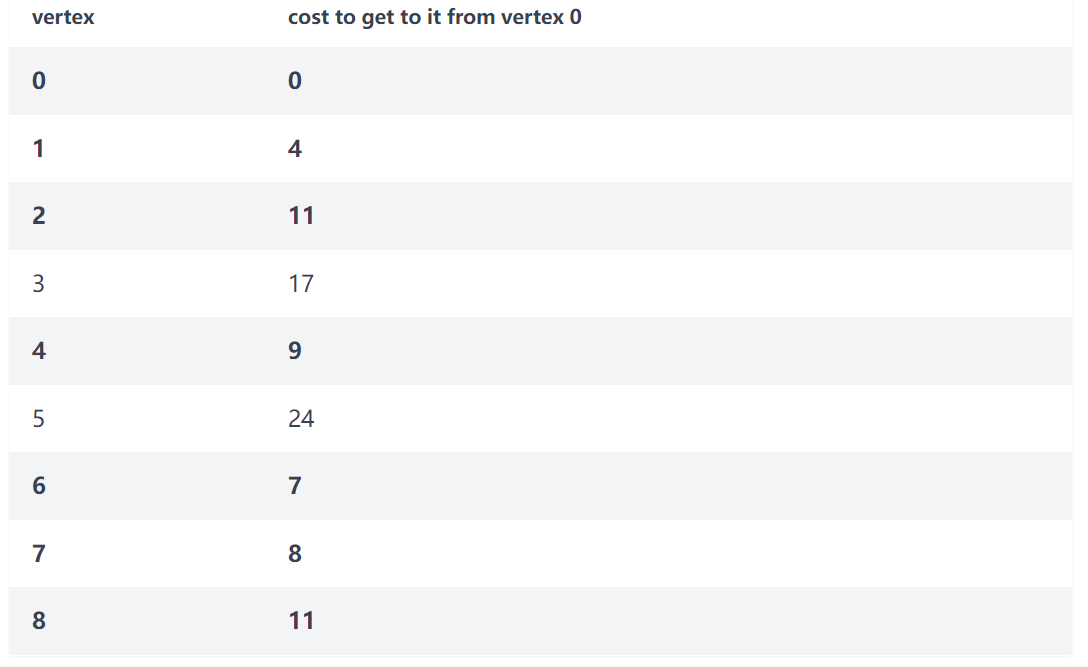
结果:
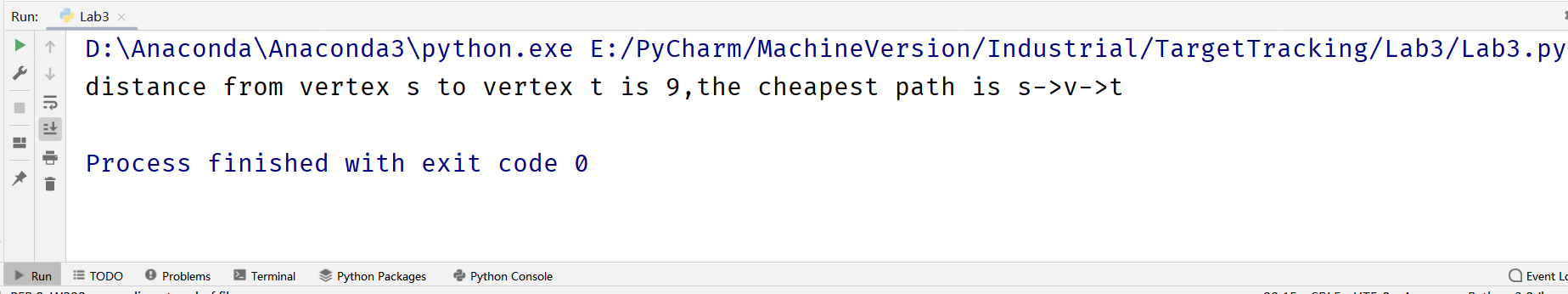
测试 得到节点s和t之间的最短路径。
self.edges[v][u] = weight 即可。为了实现方便,图中节点的名称并未使用字符表示,而是使用数字进行表示,在搜索完之后根据字典再对应回去。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 from queue import PriorityQueueclass Graph : def __init__ (self, num_of_vertices ): self.vertices = num_of_vertices self.edges = [[-1 for i in range (num_of_vertices)] for j in range (num_of_vertices)] self.visited = [] def add_edge (self, u, v, weight ): self.edges[u][v] = weight def dijkstra (self, start_vertex ): D = {v: float ('inf' ) for v in range (self.vertices)} D[start_vertex] = 0 pq = PriorityQueue() pq.put((0 , start_vertex)) previousVertex = {} while not pq.empty(): (dist, current_vertex) = pq.get() self.visited.append(current_vertex) for neighbor in range (self.vertices): if self.edges[current_vertex][neighbor] != -1 : distance = self.edges[current_vertex][neighbor] if neighbor not in self.visited: old_cost = D[neighbor] new_cost = D[current_vertex] + distance if new_cost < old_cost: pq.put((new_cost, neighbor)) D[neighbor] = new_cost previousVertex[neighbor] = current_vertex return D, previousVertex def Dijkstra (): g = Graph(6 ) g.add_edge(0 , 1 , 6 ) g.add_edge(0 , 3 , 3 ) g.add_edge(0 , 2 , 5 ) g.add_edge(1 , 4 , 3 ) g.add_edge(1 , 3 , 1 ) g.add_edge(2 , 3 , 1 ) g.add_edge(2 , 5 , 2 ) g.add_edge(3 , 4 , 7 ) g.add_edge(3 , 5 , 9 ) g.add_edge(5 , 4 , 5 ) D, previousVertex = g.dijkstra(0 ) dic = {0 : 's' , 1 : 'v' , 2 : 'u' , 3 : 'w' , 4 : 't' , 5 : 'z' } path = [] cheapest_path = [] key = 4 while True : if key == 0 : path.append(0 ) break else : path.append(key) key = previousVertex[key] for point in path[ : : -1 ] : cheapest_path.append(dic[point]) cheapest_path = "->" .join(cheapest_path) print (f"distance from vertex {dic[0 ]} to vertex {dic[4 ]} is {D[4 ]} ," f"the cheapest path is {cheapest_path} " ) if __name__ == '__main__' : Dijkstra()
结果: